045. The Uniform Distribution
A Uniform distribution is a continuous distribution in which every possible outcome has an equal chance of occurring. The experiment of rolling a die is an Example. The probabilities of all possible outcomes are all 1/6 (numbers 1 to 6). The number that actually occurs in a single roll is an observation, while the outcome of the roll is a random variable and can take any value from 1 to 6.

Figure 4.4 – A Uniform Probability Distribution for Rolling a Die
The Mean of a uniform distribution is halfway between its two end points (A – minimum or a lower end point of distribution, B – maximum or an upper end point of the distribution)

Figure 4.5 – A Uniform Probability Distribution
![]() . (4.17)
. (4.17)
The Standard deviation of a uniform distribution is
![]() . (4.18)
. (4.18)
The Total area under the curve must equal 1 or 100 percent. Since the area is height times width, the height is
![]() , (4.19)
, (4.19)
Where B – a is the width or range of the distribution.
The probability of a single observation between two values X1 and X2 can be determined as in Formula (4.20)
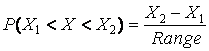 . (4.20)
. (4.20)
| < Предыдущая | Следующая > |
|---|