076. Coefficient of Correlation
Designated as R, the correlation coefficient is simply the square root of the coefficient of determination. Developed by Karl Pearson around the turn of the century, it is sometimes called the Pearsonian product-moment correlation coefficient.
Thus,
R = ![]() .
.
The value for r ranges between +1 and -1. The correlation coefficient must be given an algebraic sign after calculating. As it reflects the slope of the regression line, the sign of R is the same as the regression coefficient B1. Thus,
· If R > 0, B1 will be positive and the line will slope up.
· If R < 0, B1 will be negative and the regression line will be negatively sloped.
· If R = 0, no linear relationship between X and Y is suggested.
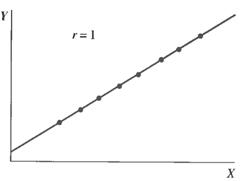
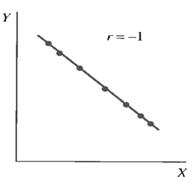
· The absolute value of R (|R|) indicates the strength of the relationship between X and Y (Fig. 7.10).
|
A |
B |
|
C |
Figure 7.10 – Potential values for R: A – Perfect positive correlation;
B – Perfect negative correlation; C – No linear correlation
| < Предыдущая | Следующая > |
|---|